If you look at a snake, you may notice that they do not have visible ears. This may leave you wondering if snakes can even hear at all.
Can snakes hear?
Snakes do have some hearing. While they can’t hear airborne sounds very well, they have the ability to hear vibration through the ground. They can also hear airborne sounds if it vibrates the snake’s head.
Snake Anatomy
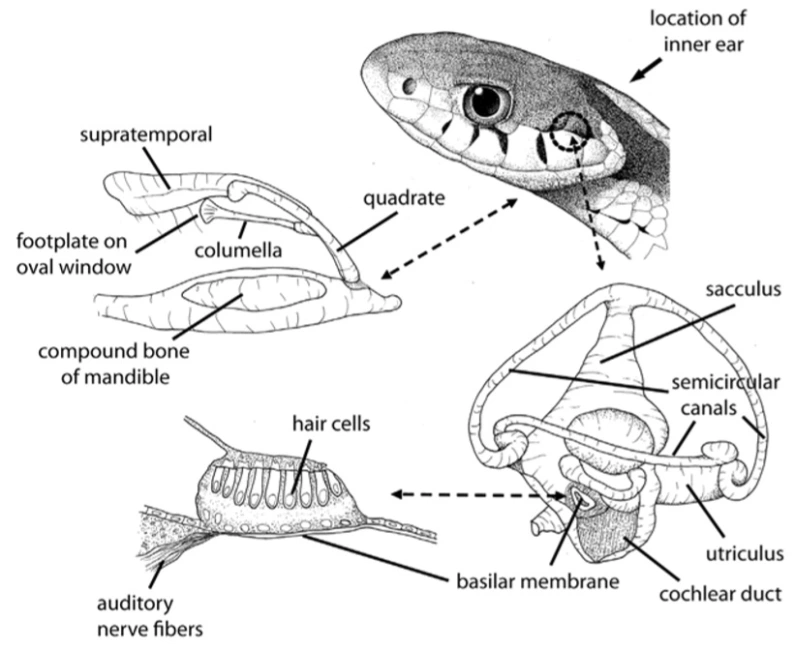
While lizards have obvious holes to hear through, snakes lack this. In mammals, we use a tympanic membrane to help us hear sounds in the air.
Snakes lack this structure and instead rely on other systems. According to this study, snakes hear with the cranial nerve, inner ear, and somatic system.
This means that snakes hear very differently than humans.
They hear a much narrower range of sound. Snakes are more sensitive to vibration through the ground such as footsteps and less sensitive to softer sounds in the air.
If you are wondering if a snake could hear a sound, try feeling if you feel any vibrations from the sound. If you can feel it, a snake can hear it.
This is because snakes hear primarily through vibration in their skull and jawbones. They hear best when their head is on the ground, but they can hear any sound that vibrates their skull.
How Snakes Use Hearing

Snakes typically hunt using their strong sense of smell or the heat-sensing some genera like pit vipers, boas, and pythons have. Most snakes have much better vision than hearing, though smell is their main sense in the majority of species.
Diurnal species have better eyesight on average, but all snake species have about the same level of auditory sensitivity. While snakes do have reduced hearing, they still show consistent responses to both airborne and ground-borne sound vibrations.
According to this study, snakes also use sound for Batesian mimicry. You may be familiar with this form of mimicry. For instance, a non-toxic butterfly may mimic the colors and pattern of a toxic butterfly to discourage predators.
Snakes also use this. Many snakes mimic the colors of coral snakes or other venomous snakes in their range. Batesian mimicry can also include sound.
In this case, snakes that share a habitat with rattlesnakes will rustle their tail in the brush to mimic the sound of a rattlesnake’s characteristic rattle.
Most sounds produced by snakes are likely not to communicate with other members of their species. The most common sounds from snakes are behaviors like hissing and using mimicry.
However, this does not mean that some species of snake may not ever use sound to communicate with other snakes of the same species. Snakes do react defensively to sounds.
Captive Snakes and Sound

Captive snakes may be stressed out if they are in a loud room. They can also seem to hear at least some sounds that prey can make. Ball pythons have been proven to hear low frequencies well (see my ball python enclosure setup and care sheet).
This means that they can likely hear music with heavy bass. They can also likely hear louder and deeper voices. If you notice your snake becoming stressed for seemingly no reason, it may be sound.
Listening to loud music, a loud television, or loud conversations could be disturbing your snake. If you thought snakes were completely deaf, you may not realize this could be a factor.
Try keeping your stressed-out snake in a quiet room and avoid any loud sounds or heavy bass in the room.
This may help your snake relax. If the enclosure is against a wall, place your hand on the wall. If the sound from a sound system or television on the other side of the wall is vibrating the wall, your snake may hear it.
Appliances like air conditioners can also create low frequencies that you can’t hear very well but may produce disturbing vibrations that would bother a snake that cannot escape them.
Since snakes can’t escape the noise, it will stress them out.
Noise Pollution and Snakes

Since snakes are typically considered virtually deaf, little has been noted on whether noise pollution affects wild snakes like it can for other species.
This case study from 2020 noted unusual behavior in an Indian rat snake (Pytas mucosa). The snake was observed fleeing during a period of loud sound.
Even though the sound was mainly airborne, the snake still attempted to flee. This brings up questions of how noise pollution affects wildlife.
The effects of noise pollution on birds is understood, but poorly studied in snakes. Since snakes can hear loud sound, it is entirely possible that noise pollution can affect snakes and disturb them.
The construction of areas where there will likely be loud noises like major roads, concert venues, airports, and sport stadiums can easily disturb wildlife. This includes snakes thanks to new understanding of how their hearing works.
Conclusion
Snakes can hear much better than you would think. They are most sensitive to vibrations through the ground. They can hear loud sounds in the air.
This is through vibration. If you can feel a vibration caused by sound, your snake can likely hear it as well. This means that snakes will be disturbed by loud sounds like music or car engines.
If you have any questions, please leave a comment below. If you have any experience with a pet snake hearing sounds you wouldn’t expect, please leave it below as well.




